Overview
In order to conduct Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transactions with a trading partner, businesses need a way of transmitting their EDI messages. Today, we take a look at the most widely used EDI transmission types, their main characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
VAN or Direct
Generally speaking, when conducting EDI transactions with a trading partner, there are only two sets of options for transmitting EDI messages. The first option involves a third party service known as a VAN or Value Added Network, while the second option does not. In the second option, known as the Direct or Point-to-Point method, two trading partners connect directly with one another through an agreed communication protocol such as FTP, FTPS, SFTP, AS2, or OFTP.
Actually, you will still need to select an EDI communication protocol if you transact through a VAN. The main difference with connecting directly is that, when you use a VAN, you will generally only need one protocol – the protocol for communicating with the VAN.
Connecting through a VAN
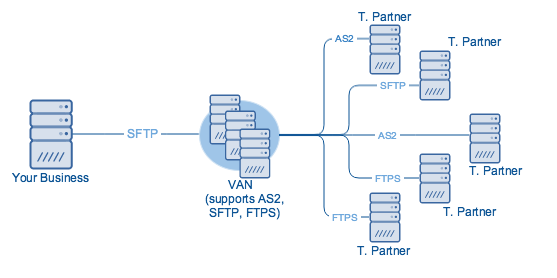
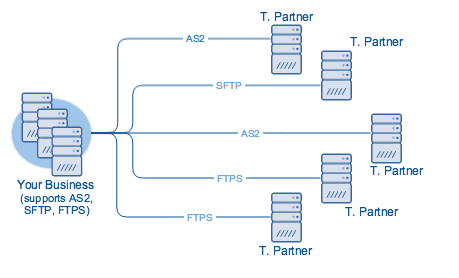
On the other hand, if you use a direct method, you will likely need more than one protocol because you’ll probably have to transact with multiple trading partners and not all trading partners will be using the same protocol.
Connecting Directly
In our list below, we introduce you to the VAN option and then proceed with the 5 most popular EDI communication protocols, all of which you can see when you request a free trial of JSCAPE.
1. VAN
A VAN or Value Added Network, which is now more commonly known as an EDI Network Services Provider, is a third party service that acts as an intermediary between trading partners. These providers typically charge via a pay-as-you-go, monthly, or annual subscription model. VANs free businesses from some of the hassles in setting up the EDI communications infrastructure.
One of the most important things to consider when choosing an EDI communication protocol is whether your trading partners already use it. If they don’t and you really prefer a particular protocol, you would need to convince them to adopt your protocol of choice.
Things can get more complicated if you have more trading partners to transact with (which will likely be the case) because each trading partner would have its own preferred protocol.
VANs enable you to eliminate this interoperability issue because they normally support a wide range of protocols. There’s a good chance they already support your preferred EDI transmission protocol as well as the preferred protocols of your respective trading partners.
While a VAN might look like the easier option, it’s not suitable for those organizations who want to have more control over their transactions and data. In addition, VANs generally cost more. Costs can increase further as your transactions and document workloads go up.
The advent and subsequent ubiquity of the Internet opened the doors to more affordable and easily accessible methods of transmitting EDI. The remaining 5 protocols on this list all run on the Internet.
2. FTP
FTP is a general purpose file transfer protocol often employed for bulk file transfers. An FTP server is readily installed in all major operating systems, including Windows, Linux, UNIX and Mac OS X, so accessibility is not a problem. In existence for over 40 years now, FTP is probably the most widely used file transfer protocol on this list.
One problem with FTP is that it lacks the necessary security features to protect sensitive information. When you transmit personal information, financial data, product data, pricing information, and other kinds of confidential information, your communications medium must have security capabilities like encryption, authentication, and data integrity. To address this problem, some trading partners run their FTP transactions over a VPN (Virtual Private Network).
3. FTPS
To address the security limitations of FTP, the people developing the protocol incorporated a couple of security features in later versions. The result was FTPS. FTPS connections are protected by SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer or Transport Layer Security). SSL/TLS addresses confidentiality and authentication issues through data-in-motion encryption and digital certificates/signatures respectively.
Related articles:
SSL vs TLS – Know The Difference
4. SFTP
Like FTPS, SFTP also has the ability to establish confidentiality and authentication. But while FTPS relies on SSL/TLS for security, SFTP relies on SSH (Secure Shell), the same protocol used for secure remote logins.
Related articles:
Install A Linux SFTP Server Via Command Line and Configure Via Web UI
Business Benefits Of An SFTP Server
Preparing Trading Partner Servers For SFTP Automation
5. AS2
Both FTPS and SFTP can be very secure. However, like FTP, they’re really general-purpose file transfer protocols. Business transactions usually require a couple more functions. For instance, when you carry out a transaction, you’ll usually want it supported by some form of receipt. Neither FTPS nor SFTP are capable of providing that.
That’s where specialized file transfer protocols can come into play. One protocol that already comes with an electronic receipt is AS2 (Applicability Statement 2). AS2 provides digitally signed electronic receipts through what are known as MDNs or Message Disposition Notifications.
Actually, AS2 was specifically created for Electronic Data Interchange. Because it runs on HTTPS, which is protected by SSL/TLS, AS2 offers the same security features as FTPS but with the added benefit of an MDN.
Related articles:
The Quickstart Guide To Setting Up An AS2 Server
How To Set Up An Automated AS2 File Transfer
6. OFTP
Another protocol that’s closely associated with EDI is OFTPor the Odette File Transfer Protocol. Like AS2, OFTP was purposely built for businesses. In other words, it’s also capable of providing digitally signed electronic delivery receipts.
So which one is more suited for EDI? AS2 or OFTP? When choosing between the two, it usually depends on your industry and geographical location. OFTP is more common in Europe, especially in the auto industry. On the other hand, if your transactions are going to be in the US, then AS2 would be the better choice. AS2 is the de facto standard for EDI transactions in the US.
There may of course be instances when you’ll need both, like if you’re an electronics company supplying components/parts for car companies as well as other manufacturers.
The problem with direct connections
Using direct connections for your EDI transactions can help you save on costs. It will also allow you to have more control of your data. Perhaps the biggest problem is that you’ll have to deploy several file transfer services. If you have multiple trading partners and they’re not using the same transmission protocol, then you’ll need to install a server for each required protocol.

That can obviously complicate matters.
Connecting directly with a MFT server
One way to address this problem is by using a managed file transfer server. An MFT server supports multiple protocols. JSCAPE MFT Server, for instance, supports all major protocols used in EDI transmissions, including FTP, SFTP, FTPS, AS2, and OFTP. It even supports other protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, WebDAV, and AFTP.
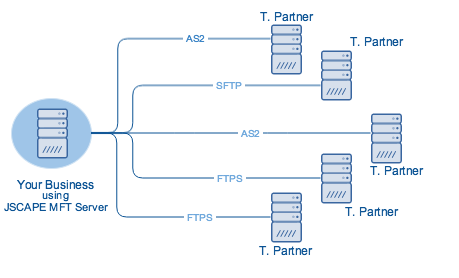
MFT servers likewise have built-in features for automation and other security functions.
By using a single solution for transacting with all your trading partners, you can greatly simplify B2B integration and security, improve transaction visibility and control, and reduce overall costs.
Get Started
Would you like to try a managed file transfer server for free? Request a free trial of the JSCAPE MFT Server which comes with a fully-functional evaluation edition. To try it out, just click below.





