Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) and Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) are both widely accepted alternatives to the enduring but highly vulnerable File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Since both protocols run on Secure Shell (SSH), IT professionals working with SSH-oriented platforms, such as Linux or UNIX, are often faced with the dilemma of choosing between the two when implementing secure file transfers. If you’re in a similar predicament, this post should help you make the right choice.
Here, you’ll find nine key comparisons between SCP and SFTP that will help you pick the right protocol for your specific use case. Before we start comparing these two, let’s define them first.
What is SCP?
As its name suggests, SCP is primarily used to copy files between hosts. Although, like SFTP, SCP is typically delivered through an SSH server, SCP is an entirely different protocol. SCP is actually derived from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) program Remote Copy Protocol (RCP). It was designed to address the vulnerabilities in RCP, while retaining RCP functionality.
In fact, even if SCP also obtains its security features from the underlying SSH network protocol, SCP commands share more similarities with RCP commands than with SFTP commands. Check out these examples that introduce you to the SCP command line. Notice how those commands are relatively less sophisticated than SFTP commands.
What is SFTP?
Also known as SSH File Transfer Protocol, SFTP is a more advanced SSH-based file transfer tool. You’ll understand what we mean by “more advanced” as you read through this post. Like SCP, SFTP uses SSH for its security features. The commands you use for uploading and downloading files during an SFTP session are specific to SFTP. However, the data transfer itself is carried out through an encrypted SSH connection.
SCP vs. SFTP comparisons at-a-glance
We’re now about to compare SCP and SFTP using various criteria. Before we proceed though, we’d like to share a summary of those key comparisons. You can review the details in the succeeding sections.
| Properties | SCP | SFTP |
| Speed | ✅ Generally faster | Generally slower |
| Security | Slightly less secure | ✅ Slightly more secure |
| Functionality | Fewer capabilities | ✅ More capabilities |
| Reliability | Less reliable | ✅ More reliable |
| Support for large files | Less capable | ✅ More capable |
| File management | Less capable | ✅ More capable |
| Platform compatibility | ✅ Same | ✅ Same |
| Resource consumption | ✅ Lower consumption | Higher consumption |
| Ease of use | Depends on the use case | Depends on the use case |
1. Speed
SCP has fewer capabilities compared to SFTP. On the flip side, its lower overhead results in faster file transfers. For instance, SCP doesn’t acknowledge every single packet the way SFTP does. Because it doesn’t have to wait for packet confirmations, SCP performs even faster in high-latency networks. If you simply want to copy files to a remote host and don’t have to perform additional tasks, like changing directories or creating new ones, use SCP.
2. Security
Both the SCP and SFTP protocols derive most of their security features from SSH. This includes features and functionality like data-in-motion encryption, public key authentication, cryptographic algorithms and data integrity. That being said, SFTP does have a few security-related features that are not found in SCP.
For instance, only SFTP has the capability to set file permissions (e.g., using the chmod command), which limits what users can do to certain files. Moreover, because SFTP acknowledges every single packet while SCP does not, SFTP is less prone to packet loss.
3. Functionality
When it comes to functionality, SFTP is the far better protocol. The SCP protocol is only good for basic data transfers. However, if you need to do additional tasks on the remote server, such as create new directories, change working directories, view directory listings and set file permissions, you should use SFTP.
4. Reliability
SCP and SFTP both operate on top of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). This essentially means they both benefit from TCP’s reliability features. That said, it’s important to understand how this reliability mechanism works. Indeed, TCP retransmits lost packets. However, this retransmission only applies during the duration of an active transfer. If a transfer is interrupted (e.g., due to a network outage or disconnection), TCP’s retransmission no longer applies.
At that point, it’s up to the application layer protocol (in this case, SCP or SFTP) to handle the issue and complete the transfer. In the case of SCP, you have no choice but to restart the transfer from the beginning. SFTP, on the other hand, handles the issue more elegantly. It allows you to resume the transfer from the point where it was interrupted. Therefore, when viewed in this context, SFTP can be considered a more reliable protocol.
5. Support for large files
SFTP’s superior reliability makes it more suitable for large file transfers. While SCP theoretically allows you to transfer large files faster, this advantage can only be experienced in perfect network conditions. If an external factor somehow interrupts your file transfer, which often happens when transferring large files, you’ll have to start all over again if you’re using SCP.
With SFTP, you can simply resume that large file transfer. For instance, in an SFTP command line client, you can accomplish this by issuing the reget or reput commands. When you execute these commands, SFTP checks the target system for partially written files and continues from the point it was interrupted. Thus, while SFTP may be slower, it’s technically more capable of supporting large files.
6. File management
As you’ve probably gathered from the previous sections, SFTP has superior file management capabilities. You can perform tasks on the remote file system similar to the ones you typically do locally. For instance, you can display directory listings, create new directories, rename existing directories and so on.
These tasks aren’t natively supported in SCP. In fact, even seemingly basic tasks, such as deleting a file, aren’t possible directly through SCP. You can, however, work around these limitations by using graphical multi-protocol clients like WinSCP, which provide added functionality on top of SCP features.
7. Platform compatibility
Most SCP and SFTP deployments use OpenSSH, a widely used, open-source implementation of SSH. OpenSSH is now supported by all major operating systems, including Windows Server, Linux and UNIX. So, you won’t have any problem using either SCP or SFTP. They’re now both easily accessible.
8. Resource usage
Compared to a typical SCP session, an SFTP session may involve several tasks. Consequently, an SFTP session may consume more compute resources on your server compared to an SCP session. The disparity between the two is amplified in production environments, where the server has to handle multiple concurrent connections. In these environments, resource consumption on an SFTP server will be substantially higher.
9. Ease of use
Although SCP supports fewer commands, it doesn’t necessarily follow that it’s easier to use. Well, if all you need to do is upload or download files, then perhaps you can make an argument that SCP is easier since its commands are shorter. For example, here’s an SCP command that uploads a file to a remote host:
scp file.txt user@remotehost:/path/to/destination/
The equivalent SFTP command would be:
sftp user@remotehost
put file.txt /path/to/destination/
As you can see, SFTP requires two lines, while SCP only requires one.
However, if you want to perform other tasks, such as changing the working remote directory or renaming a remote directory, you’ll need to incorporate workarounds to achieve those tasks with SCP. Thus, it really depends on the use case.
Perform SCP and SFTP file transfers with a single solution
While SCP and SFTP have their advantages and disadvantages, they don’t have to be mutually exclusive all the time. Even if SFTP is suitable for a wider range of use cases, there can be instances when you might prefer to use SCP, such as file transfers between internal hosts with pre-configured target directories or automated backups to a network attached storage (NAS).
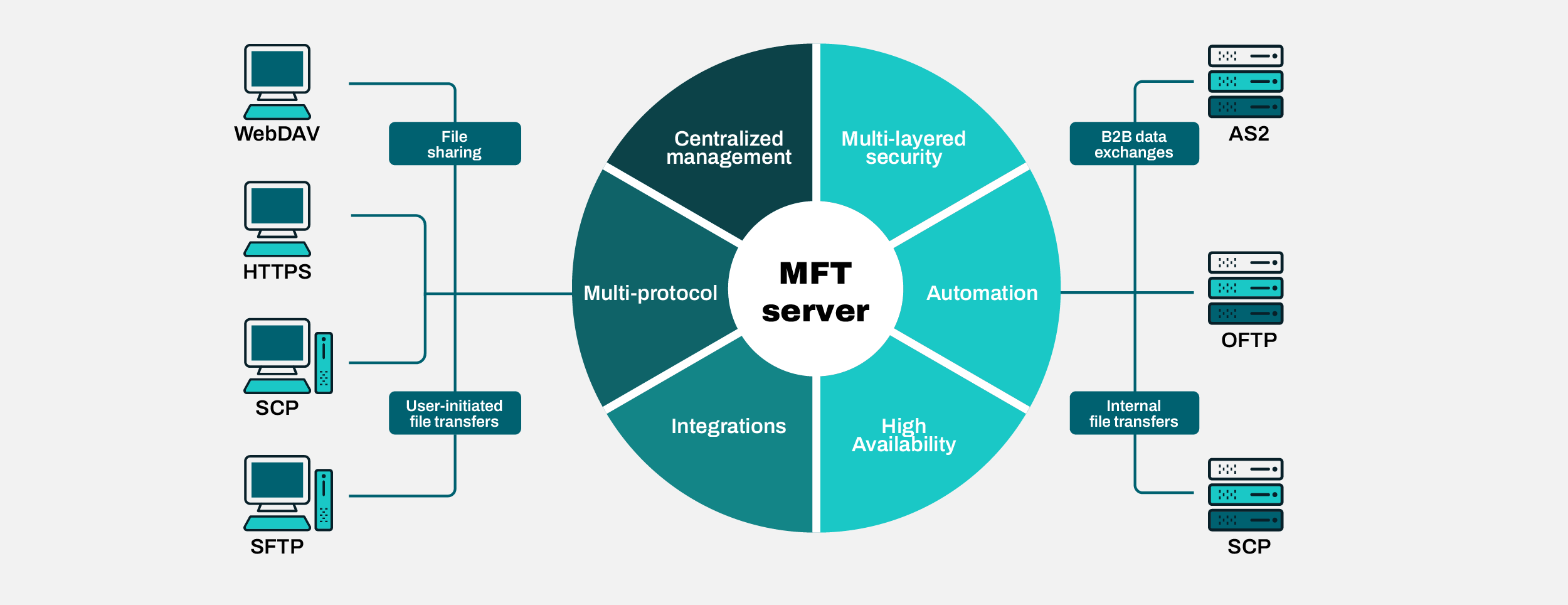 If you somehow need to support both SCP and SFTP, or perhaps other file transfer protocols for that matter, you can use a managed file transfer solution like JSCAPE MFT Server by Redwood. JSCAPE MFT Server can simultaneously act as an SCP and SFTP server. It can even simultaneously support other file transfer protocols, such as:
If you somehow need to support both SCP and SFTP, or perhaps other file transfer protocols for that matter, you can use a managed file transfer solution like JSCAPE MFT Server by Redwood. JSCAPE MFT Server can simultaneously act as an SCP and SFTP server. It can even simultaneously support other file transfer protocols, such as:
- Applicability Statement 2 (AS2)
- File Transfer Protocol Secure (FTPS)
- Odette File Transfer Protocol (OFTP)
- Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV)
- And others
JSCAPE supports user-initiated file transfers as well as file transfer workflow automation use cases. If you would like to see how everything works, you may schedule a quick demo of JSCAPE now.





