10 Ways to Make Server to Server File Transfers for Enterprise Use

Overview
Server to server file transfers are usually associated with enterprise business processes. Interestingly, some of these file transfers actually don't fit the bill. In this post, we'll share some tips on how you can enhance your server to suit the stringent requirements of the enterprise.

1. Take advantage of business process automation
Automation is one of the essential attributes of a true server to server file transfer system for enterprise businesses. If your file transfers still require considerable human intervention, then you have got to change that. Automation can eliminate human errors, keep you on schedule, and improve efficiency.
Let me give you an example. Let's say you need to transmit electronic documents to three trading partners every week. The first set of documents has to be sent to one trading partner every Monday, the second set to another trading partner every Wednesday, and the last set to a third trading partner every Friday.
Since these are presumably large sets, it wouldn't be advisable to send them during office hours, when they could clog the network and disrupt regular business transactions. But would that mean you would have to assign someone to send those files every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday night? What if that person gets sick or simply forgets to do his job? If those documents are critical to your trading partners' business processes, you could have a serious situation in your hands the next day.
Not if you employ automation. With an automated file transfer, you can simply set those transmissions to fire off by themselves at pre-set schedules. You can even configure the system to send a notification email or Twitter tweet once the transmission completes or if something requires attention.
2. Integrate with your EDI system
Companies who regularly transact with other companies, frequently exchange electronic documents. These transactions are usually done through email or manual FTP. To address the problem of incompatible data formats, some of these companies employ electronic data interchange or EDI.
If you use EDI, you can significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of your EDI exchanges by transmitting your EDI documents via server to server file transfers. A server to server file transfer can automate your exchanges and, if carried out over AS2, can secure your EDI documents as they traverse the Internet. In addition, an AS2 connection can be configured to provide an electronic return receipt known as an MDN (Message Disposition Notification), which can help you determine whether the transmission completed successfully.
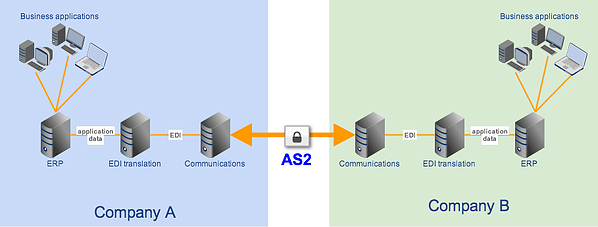
Integrating your EDI system with your file transfer server can be a breeze if your server is already built for it. If you don't know how to integrate those two, the article How To Set Up A Server To Server File Transfer should be a good place to learn what you can do at the file transfer server end (labeled "Communications" in the figure above).
3. Employ secure file transfer protocols
Enterprise file transfers typically involve significant amounts of sensitive data. Once you start transmitting personal information, trade secrets, financial data, and other sensitive information, it is your duty to make sure they're safe from unauthorized alterations or even just prying eyes.
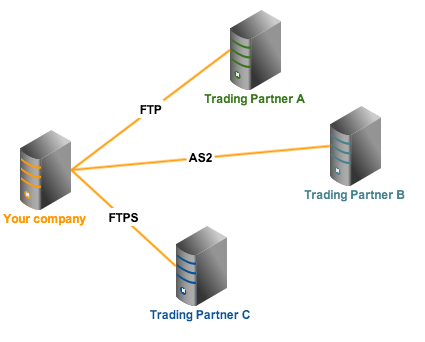
One way to do that is by employing secure file transfer protocols like FTPS, SFTP, or AS2. These protocols encrypt data in motion and prevent eavesdroppers from viewing the information you send, which is essential in complying with file transfer-impacting laws like HIPAA, SOX, GLBA, and PCI-DSS.
Since different companies can have different protocol preferences (e.g. some prefer SFTP, while others prefer FTPS or AS2), you might need to deploy multiple protocols at the same time.
4. Use data-at-rest encryption
It isn't enough to only encrypt data in motion. Once files reach your server and get stored there, it would again be your duty to secure them. This can be done using data at rest encryption methods like OpenPGP. By encrypting sensitive files stored in your server, you can prevent crooks from obtaining any information stored in those files even if they succeed in stealing the server's hard disk or the entire server itself.
5. Adopt strong authentication and access control
If your server to server file transfers involve high volumes of sensitive information, your server can become a high-value target. Hackers will want to infiltrate your server to get to your data. Although there are many ways of hacking into a server, most methods involve obtaining user account login credentials and then using those credentials to get in.
To make it more difficult for hackers, you should implement strong authentication and access control mechanisms. Multiple layers of protection is always a good strategy. For instance, you can apply a combination of these various authentication and access control methods:
✔ Digital certificates/private keys
✔ LDAP, NTLM, or PAM
✔ Two-factor authentication using mobile phones
✔ IP-based access control
✔ RBAC and
✔ a strong-password policy
6. Enable Data Loss Prevention
Although encryption is a very important security method (it is usually your best friend in achieving compliance), it also increases the size of your files and consumes a relatively larger amount of computing resources. Thus, you might want to do selective encryption, i.e., encrypt only files containing sensitive information.
But in order to implement selective encryption, you would have to determine which files contain sensitive data. It would be very costly and time-consuming if you did things manually. A more efficient option would be to apply Data Loss Prevention or DLP. DLP can automatically detect strings of text that follow a particular pattern. For example, you can configure a DLP to detect credit card numbers.
For a comprehensive discussion on the subject, we recommend the 3-part article Using DLP to Protect Credit Card Data. It includes a tutorial on how you can set your server to 1) automatically encrypt files containing credit card numbers and 2) send an email notification regarding the detection.
7. Set up automated virus scans
Viruses are among your worst enemies. A single virus can easily cause a massive infection on an enterprise file transfer server, where a large number of business-critical files converge. And since these servers are used for sharing files, an infected server can likewise easily wreak havoc throughout your organization.
It is therefore imperative that you act upon a virus infection before it spreads. The article Automating FTP Virus Scans with Kaspersky Antivirus is one of several articles on this site that details how you can automatically detect a virus on your server, delete/quarantine the infected file, and send out an email notification regarding the detection.
8. Implement high availability
Being the central hub for data exchanges between staff, departments, branches, and trading partners, your file transfer server is undoubtedly mission critical. If it goes down, several business processes will be affected.
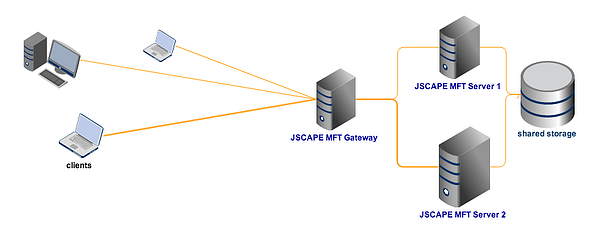
To minimize (if not totally eradicate) downtimes, you need to deploy a highly available server. This would entail setting up at least one more machine (a failover server) that can automatically take over the moment the production server goes down. We have a wide collection of articles that can help you set up high availability file transfer services. Click that link to view them all.
High availability file transfer with shared storage
9. Counter poor network conditions inherent to WANs
As a large company with a global reach, you will need to transfer files to other continents. To reach their destinations, transmitted files would have to traverse Wide Area Networks (WANs) where they can be subjected to poor network conditions like latency and packet loss.
High latency and packet loss can bring file transfer speeds down to just 10% of a network's full potential. This can cause considerable delays and missed opportunities. Furthermore, the longer a connection transmitting sensitive data has to stay connected, the more vulnerable it becomes to possible threats.
One way to counter these network conditions is by transmitting files through UDP-based protocols like AFTP. AFTP is immune to network conditions like latency and packet loss. To learn more about AFTP (Accelerated File Transfer Protocol) and its applications, click that link and read the articles found there. You may also download the White Paper How to Boost File Transfer Speeds 100x Without Increasing Your Bandwidth.
10. Activate logging
Corporate governance policies require companies to implement logging procedures which would enable IT systems to be easily auditable. This can come in handy if something goes wrong. For example, if a data breach occurs, data forensics experts will want to find traces of the culprit through recorded activities/events on your server. This can be found on system/event log files. But if your logs aren't detailed enough, they won't have enough clues to start with.
Summary
There, although that is by no means an exhaustive list, it certainly includes the most important tips for boosting your server to server file transfers. Want to know whether a server to server file transfer is something you'd need? Click that to find out.
Request a trial
Not all file transfer servers are suitable for enterprise-grade server to server file transfers. If you want to test it out, we recommend getting started with a risk-free trial of
JSCAPE Managed File Transfer Server.