Choosing Between SSL Implicit, Explicit, and Forced Explicit Modes

Overview
There will be times when you'll want to transfer files over a secure connection. One option is to use FTPS (FTP over SSL) which provides data-in-motion encryption through SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). When you setup an FTPS service in JSCAPE MFT Server, you'll notice that you actually have 3 modes to choose from explicit SSL, forced explicit SSL and implicit SSL.
This post was originally published on May 6, 2012 but was updated and republished on November 4, 2018.
If you still can't tell the difference between these three SSL file transfer types, this article should enlighten you a bit; when you're ready to try it yourself, we'll get you your free trial.
Figure 1
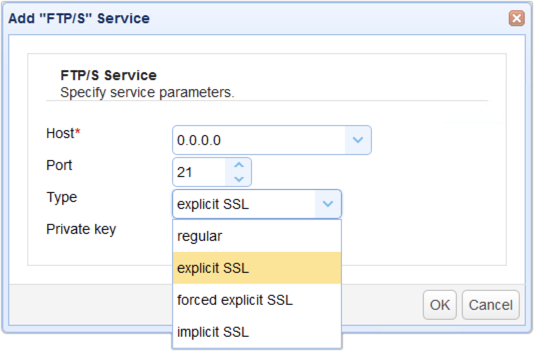
Implicit SSL
As its name implies, implicit SSL is a type of FTPS connection wherein SSL encryption is implied. As soon as a connection is established between the FTPS client and your managed file transfer server, both command (a.k.a. control) and data channels will be automatically protected with SSL encryption.
If you're not yet familiar with the two different channels used by FTP, then please see the articles Understanding Key Differences Between, FTP, FTPS, and SFTP and Active vs Passive FTP Simplified.
Implicit SSL by default uses port 990, which is different from the port (21) typically used for regular FTP.
Figure 2
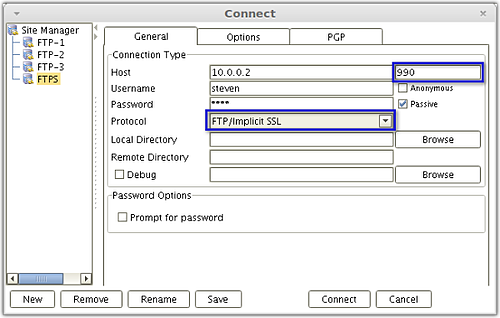
AnyClient connecting to the FTP Implicit SSL service.
Implicit SSL is ideal if you really want full encryption for your entire FTP connection from the start of the session. However, since encryption always consumes more bandwidth and computational resources, there may be instances when you'll want to encrypt only one channel.
For instance, if the files your users normally upload to your managed file transfer server don't contain confidential information, then the only things you will want to encrypt are the usernames and passwords that get submitted during authentication. Since user credentials are sent via the command channel, then that's the only channel you would need to encrypt.
But then you can't do that with Implicit SSL. Implicit SSL always encrypts both the command and data channels.
We also recommend: TLS vs SSL - Know The Difference
Explicit SSL
For the situation described above (encrypt only user credentials), a better choice would be Explicit SSL. With Explicit SSL, you're allowed to choose which channel to encrypt. You can even choose to revert back to regular (unencrypted) FTP and not encrypt any channel at all. Explicit SSL runs over port 21, which is the same port used by regular FTP, making it easy for your server to cater to both clients that support FTPS and those that only support regular FTP.
Most secure file transfer clients will encrypt both command and data channels of Explicit SSL connections by default. This is the better choice, especially for organizations covered by laws and regulations like PCI-DSS, SOX, HIPAA, and GLBA, which either strongly recommend or explicitly require encryption.
If you're working to achieve regulatory compliance, you wouldn't want to leave security decisions in the hands of your end users. In that case, it would certainly be more prudent to encrypt data channels at all times.
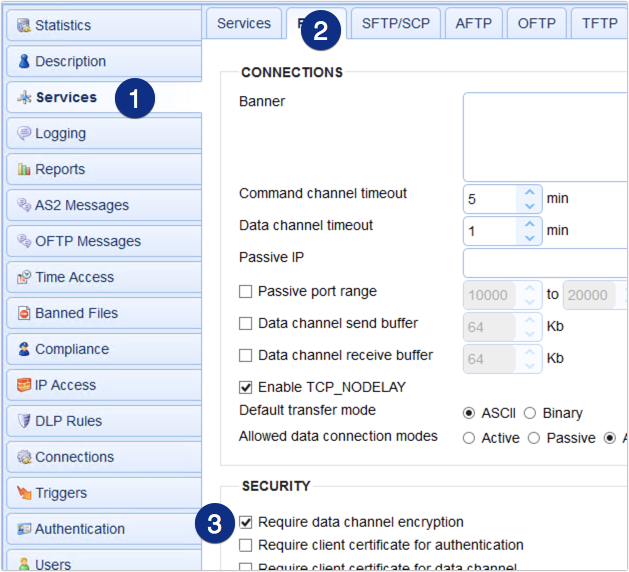
To make sure all clients are forced to use encrypted data channels when connecting to your Explicit SSL FTPS service, go to the Services > FTP/S node in JSCAPE MFT Server and scroll down until you see the checkbox labeled Require data channel encryption. By enabling this option if a user tries to disable data channel encryption, your server will not allow the session to continue.
Figure 3
As mentioned earlier, if you have FTPS service of type Explicit SSL running on your server, you can connect to that service using either an SSL-protected FTP connection or a regular FTP connection.
Figure 4
Figure 5
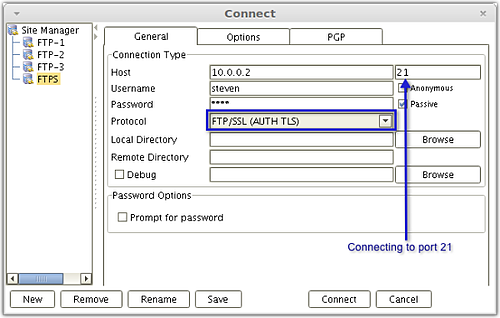
AnyClient connecting to the FTP Explicit SSL service using an SSL-protected FTP connection.
Figure 6
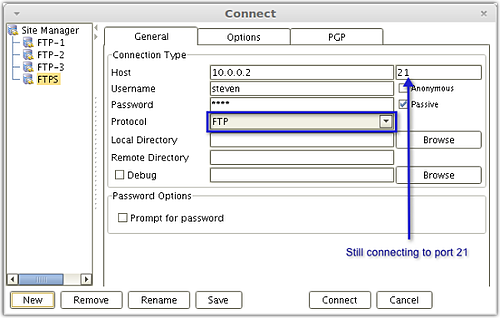
AnyClient connecting to the same FTP Explicit SSL service using a regular FTP connection.
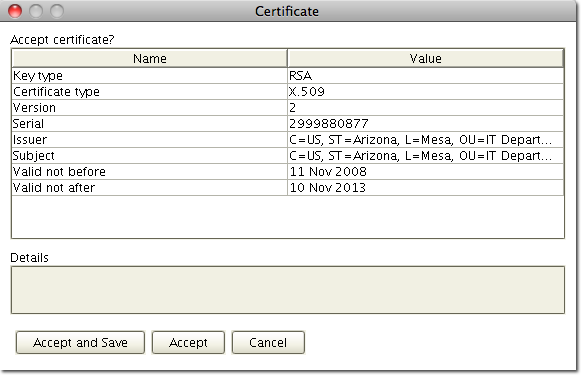
The main difference a user will notice is that the first time a user connects to a server using any variant of FTPS, they will receive a prompt to verify the digital certificate of the server. See Figure 7. This verification step is intended as a way to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. When using plain FTP no such certificate verification is displayed.
Figure 7
Forced Explicit SSL
If you really want to make sure your users' login credentials are safe from prying eyes, it's necessary to reject any client that connects using regular FTP. With regular FTP, the username and password submitted during authentication are sent in the clear, making them totally vulnerable to network sniffing tools.
In this case, you need to add the forced explicit SSL service in JSCAPE MFT Server. It works just like explicit SSL in that it allows you to choose whether to encrypt the data channel or not. But unlike explicit SSL, it requires the command channel to be encrypted prior to the user sending credentials.
Summary
Get started with your JSCAPE free trial request!
In addition, download the always free AnyClient. Download Now