10 Essential Attributes of Secure File Transfer Systems

Overview: Secure File Transfer Systems
Normally, when people send files over the Internet, they do it through email, FTP, or cloud-based file sharing services. That's perfectly fine if the files you send don't contain sensitive information. But if they do, you would have to employ a secure file transfer solution in order to prevent possible attackers from intercepting, viewing, stealing, or altering the information you transmit.

So what kind of secure file transfer solution should you be looking for? Would email encryption suffice? How about cloud-based secure file sharing? A managed file transfer service perhaps?
Bear in mind that, over the last couple of decades, both the number of threats AND the amount of information that need protection in the network have grown considerably. In other words, there are a lot of risks to mitigate, more so if you have IT-impacting regulations (e.g. HIPAA/HITECH, SOX, GLBA, PCI-DSS) to comply with.
What we have here is a list of what we think are the 10 most important attributes of a truly secure file transfer system. If your file transfers involve very sensitive information and you want to bring down your risks to a minimum, then this can serve as a checklist to achieve that.
1. Encrypts data in motion
A long time ago, I had this notion that as long as I kept my username and password to myself, whatever information lay hidden behind those login credentials was already safe from prying eyes. I applied that notion to every system I believed was adequately "protected" by a login screen - including email and FTP services.
I could have never been more wrong.
Whenever we send files through email or FTP, our information is actually sent in cleartext. Meaning, it can be intercepted along the way and viewed by anyone armed with the right tools; tools that are free and easily found on the Web. Here's one of those tools clearly displaying the username and password of an FTP user.
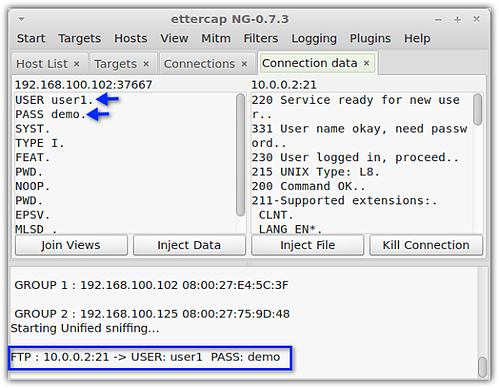
To understand how crooks use these tools, read our post on packet sniffers and encrypted FTP.
One way to protect confidential information as it is sent over insecure networks like the Internet is to use encrypted file transfer protocols like FTPS or SFTP. These data-in-motion encryption technologies render text unreadable to crooks equipped with the tools similar to the one shown above. And so, even if those crooks succeed in intercepting your files, all they'll see will be "garbled" messages like the one in the screenshot below.
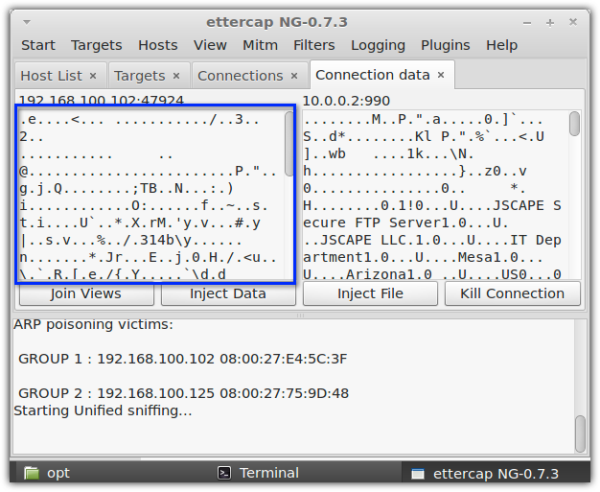
2. Encrypts data at rest
Files aren't only vulnerable during transmission. Because all these files eventually end up in file transfer servers, most malicious inviduals prefer to attack those servers instead. That's why it's important to apply encryption there as well. A server that protects files through encrypted online storage will prevent attackers from obtaining confidential information even if they succeed in infiltrating the server or in getting hold of the hard disk.
But there's one thing you should remember about these encrypted storage solutions. The location of the decryption key plays a crucial role here. If the decryption key is stored in the same location as the encrypted files and a skilled hacker finds it, it would be trivial for the hacker to decrypt your files.
You can provide better protection if you employ a public key-based technology, which will allow you to store your decryption key in a separate location. Even if the attacker manages to carry away your entire server, he won't be able to decrypt your files.
To learn more about public key encryption and how well it protects data at rest, read this post on PGP encryption.
3. Preserves data integrity
There can be instances when keeping the contents of a file confidential is not as important as preserving them. For example, you may find it alright for people to view your balance sheet but you certainly wouldn't want anyone altering it.
If data integrity is important to you, then your system should be capable of preventing or at least detecting (so the recipient will know)any unauthorized modifications.
The thing is, encryption per se cannot prevent a file from being modified. However, certain cryptographic systems already have this capability built-in, so you might want to take that into consideration when choosing a solution.
4. Supports strong authentication methods
One way a hacker can gain access to your system is by impersonating a legitimate user. If your system can be easily fooled, you're toast. To prevent this kind of attack, you system should have a strong mechanism that can accurately validate a user's identity.
There are many ways to do this. The most basic is a username and password. You shouldn't rely on that alone. You can use SSL FTP, which not only authenticates (through certificates) but also provides encryption. In addition to that, you can also deploy other authentication methods like LDAP, NTLM, or PAM.
If you want an extra layer of authentication above your usual authentication methods, I strongly recommend phone authentication. This highly advanced two factor authentication method will require your users to answer a call and confirm their desire to login. Even if a hacker manages to acquire a username and password, he won't be able to login to your server if he doesn't have the corresponding user's phone.
5. Provides multiple access control mechanisms
Normally, servers require users to enter a username and password before granting access. If the username or password is not registered on the server, the user will be denied access. For added security, some servers are equipped with an IP-based access control mechanism. If the IP address of the client requesting a connection is not in the server's list, access will be denied for that particular client. This kind of access control mechanism will allow you to restrict access from addresses you consider secure.
Another way of controlling access is by defining what folders a user or group of users can create, edit, delete, copy, upload, or download files. If your server supports it, an even better mechanism is RBAC (role-based access control), which limits users' access rights based on their roles in the organization.
6. Supports automated virus scanning
Not all crooks are out to steal information. Others just want to wreak havoc. And one way they do that on autopilot is by spreading viruses, trojans, and other malware. Some malware alter files. Others cause servers to crash or turn them into botnet zombies. That's why antivirus software should be an integral component of your secure file transfer system.
If possible, your file transfer server should have a mechanism to automatically launch your virus scanner and conduct a scan on every uploaded file. That way, you can be sure each uploaded file is checked for infections and quarantined or deleted if any malware is found.
7. Records activities in event logs
When an untoward incident like a data breach or a system crash happens, you will want to know who or what caused it. In cases like this, your log file is your best friend. Logs can provide valuable information to digital forensic experts once they start tracing the cause.Detailed logs can help forensics determine who accessed what and when.
Logs can also used by auditors to find out whether users are actually carrying out security best practices and to discover possible vulnerabilities.
Because of their importance in network security, system/event logs and other audit controls are required by regulations like HIPAA and PCI-DSS.
8. Forces users to adopt strong passwords
Passwords are the soft underbelly of security infrastructures. They can be pried out of unwitting users using social engineering techinques, broken using password cracking tools, or simply guessed.
Sometimes, there's not much challenge in cracking/guessing passwords because many users don't use passwords that are strong enough. For example, can you guess what the two most commonly used passwords are? They're the word "password" and "123456". I won't be surprised if you guessed them both correctly.
A password cracker in action
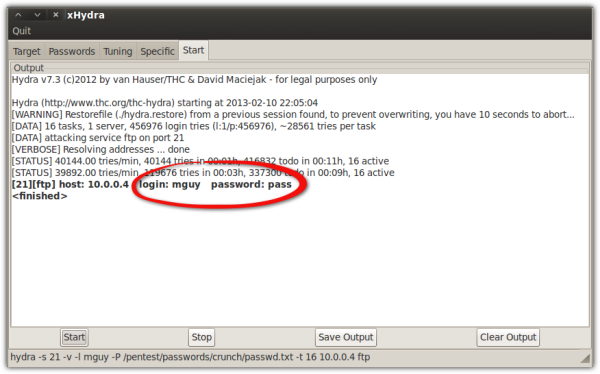
Learn more about how password crackers like the one shown above are used to crack FTP passwords.
To mitigate risks involving passwords, your secure file transfer system should be able to force (yes, it usually comes down to that) users to adopt strong passwords. Enforcing strong passwords is vital to achieving regulatory compliance. In fact, PCI-DSS has multiple requirements specifically aimed at stengthening passwords.
9. Implements data loss prevention
Implementing security measures can be a pain if you have to do things manually. You can be so much more effective and efficient if you can somehow automate virus scanning, PGP encryption, and all other business processes involving security.
Let me elaborate on this a bit in case it's still not clear to you. Let's say your business is covered by PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry - Data Security Standard). That means you have to protect all credit card information under your care. So if someone uploads a file containing credit card data onto your file transfer server, you have to make sure that information doesn't fall into the wrong hands.
Now, finding credit card data on every uploaded file is not easy - again, if you have to do things manually. That's where automation can come in handy. It would be very useful to have an automated process that can 1) detect credit card data in an uploaded file, 2) prevent any unauthorized access by encrypting the file, and 3) alert you about it.
In the infosec world, this kind of automation is called DLP or data loss prevention. If you operate in a business environment governed by regulations, DLP is certainly a must-have.
10. Supports large file transfers
How do you send large files over the Internet? If you're like most people, I bet you still send large files via email. The main problem with using email solutions for sending big files is that they are only limited up to a certain file size, mostly just a few 10s of megabytes per attachment. That's not going to be very efficient if you're going to be sending volumes of highly confidential files running up to gigabytes or even just a couple of hundreds of megabytes in size.
Legal firms doing e-discovery or movie outfits shooting films abroad are just a few of those organizations whose appetite for secure file transfers typically involve massive sizes and hence wouldn't find the maximum capacities of email adequate enough. If you're like them, then you need a secure file transfer solution that wouldn't require you to chop your files into smaller pieces or to send them out in batches.
Summary
As mentioned earlier, sensitive file transfers are now exposed to numerous risks. So, while these 10 security features are the most important, this list is still not exhaustive. Other attributes some of our clients look for in a secure file transfer include the ability to:
Redirect traffic to a failover server when the active server fails;
Perform secure server to server file transfers;
Prevent direct Internet-based access to the server; and
Meet regulatory compliance requirements
JSCAPE MFT Server is a secure file transfer solution that supports all of the attributes listed above. Give it a test run today.